All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Geophysical Survey And Remote Sensing Techniq...
- – Geophysical Surveys in Rivervale Oz 2022
- – Geophysical Surveys in Wandi Oz 2023
- – Geophysicist in Morley Aus 2021
- – Geophysicist Education in Oldsbury Oz 2023
- – Why Study Geology? in Scarborough Western ...
- – Geophysical Prospecting in Upper Swan WA 2...
Geophysical Survey And Remote Sensing Techniques in Waterford Australia 2021
(2004 ). 2011. 2011.
Bozorgnia, Yousef; Bertero, Vitelmo V. (2004 ).; Grenier, Emmanuel (2006 ). Mathematical geophysics: an intro to rotating fluids and the Navier-Stokes equations.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 59 (1 ): 183227. Defense Mapping Firm (1984 ).
Geophysical Surveys in Rivervale Oz 2022
TR 80-003. Obtained 30 September 2011. Eratosthenes (2010 ). Eratosthenes' "Location". Pieces collected and equated, with commentary and extra material by Duane W. Roller. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14267-8. Fowler, C.M.R. (2005 ). (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-89307-0. "GRACE: Gravity Healing and Environment Experiment". University of Texas at Austin For Area Research Study.
Obtained 30 September 2011. Obtained 30 September 2011.:10.
Geophysical Surveys in Wandi Oz 2023
Lowrie, William (2004 ). Merrill, Ronald T.; Mc, Elhinny, Michael W.; Mc, Fadden, Phillip L. (1998 ). International Geophysics Series.
They likewise research changes in its resources to provide guidance in meeting human demands, such as for water, and to forecast geological threats and hazards. Geoscientists utilize a range of tools in their work. In the field, they might utilize a hammer and sculpt to gather rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to search for minerals.
They also may utilize remote picking up equipment to gather data, as well as geographic info systems (GIS) and modeling software to evaluate the data gathered. Geoscientists may supervise the work of service technicians and coordinate deal with other scientists, both in the field and in the laboratory. As geological obstacles increase, geoscientists may opt to work as generalists.
Geophysicist in Morley Aus 2021
The following are examples of kinds of geoscientists: geologists study how effects of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They also may work to fix issues associated with natural hazards, such as flooding and erosion. study the products, processes, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists also, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and structure of minerals. study the movement and flow of ocean waters; the physical and chemical homes of the oceans; and the methods these homes impact coastal areas, climate, and weather condition.
They also research study modifications in its resources to supply guidance in conference human demands, such as for water, and to predict geological threats and risks. Geoscientists use a range of tools in their work. In the field, they might use a hammer and chisel to collect rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to look for minerals.
Geophysicist Education in Oldsbury Oz 2023
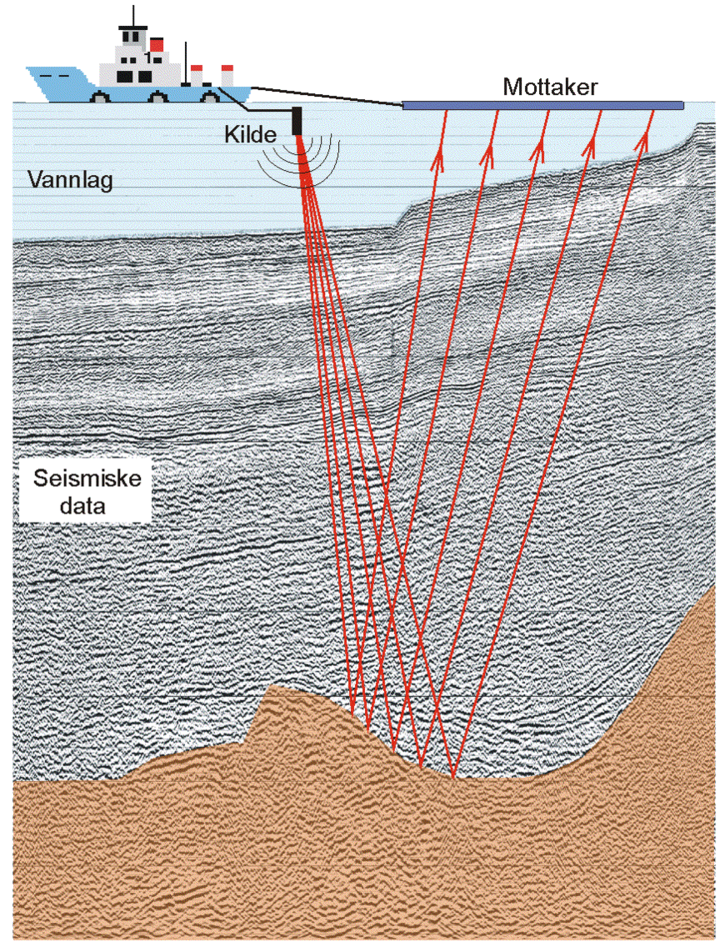

They also might utilize remote picking up equipment to gather information, along with geographic info systems (GIS) and modeling software application to evaluate the information gathered. Geoscientists may monitor the work of technicians and coordinate deal with other researchers, both in the field and in the lab. As geological difficulties increase, geoscientists might decide to work as generalists.
The following are examples of kinds of geoscientists: geologists study how consequences of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, affect the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They also might work to resolve issues associated with natural dangers, such as flooding and disintegration. study the materials, processes, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists too, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and structure of minerals. study the movement and circulation of ocean waters; the physical and chemical residential or commercial properties of the oceans; and the ways these homes impact seaside areas, climate, and weather condition.
Why Study Geology? in Scarborough Western Australia 2021
They likewise research modifications in its resources to provide guidance in meeting human needs, such as for water, and to anticipate geological threats and dangers. Geoscientists use a range of tools in their work. In the field, they may use a hammer and sculpt to gather rock samples or ground-penetrating radar devices to search for minerals.
They also may utilize remote sensing devices to gather data, as well as geographical information systems (GIS) and modeling software to evaluate the information gathered. Geoscientists might monitor the work of specialists and coordinate work with other scientists, both in the field and in the laboratory. As geological obstacles increase, geoscientists might choose to work as generalists.
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how consequences of human activity, such as pollution and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They also might work to fix issues associated with natural risks, such as flooding and disintegration. study the products, processes, and history of the Earth.
Geophysical Prospecting in Upper Swan WA 2023
There are subgroups of geologists also, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and structure of minerals. study the movement and blood circulation of ocean waters; the physical and chemical properties of the oceans; and the methods these homes impact seaside locations, climate, and weather condition.
Table of Contents
- – Geophysical Survey And Remote Sensing Techniq...
- – Geophysical Surveys in Rivervale Oz 2022
- – Geophysical Surveys in Wandi Oz 2023
- – Geophysicist in Morley Aus 2021
- – Geophysicist Education in Oldsbury Oz 2023
- – Why Study Geology? in Scarborough Western ...
- – Geophysical Prospecting in Upper Swan WA 2...
Latest Posts
Greeley-evans Area 3d Geophysical Survey in Bicton Australia 2022
Airborne Geophysical Methods in Bateman Western Australia 2022
Integrated Geophysical Surveys For The Safety in Beeliar Australia 2021
More
Latest Posts
Greeley-evans Area 3d Geophysical Survey in Bicton Australia 2022
Airborne Geophysical Methods in Bateman Western Australia 2022
Integrated Geophysical Surveys For The Safety in Beeliar Australia 2021